Buy Sodium Bicarbonate Injection Today – Secure Your Supply for Emergency & Critical Care Needs
Contact Us for Bulk Medical Orders, Hospital Inquiries, and Professional Support.
Cart subtotal
Discover premium Sodium Bicarbonate Injections—your trusted solution for acidosis treatment, pH balance, and metabolic correction. Our pharmaceutical-grade sodium bicarbonate offers rapid relief from severe metabolic acidosis, renal insufficiency, and cardiac arrest. Ideal for hospital, emergency, and clinical settings, these sterile injections help restore electrolyte balance, improve blood gas levels, and support critical care interventions. Ensure safe, effective patient management with our top-quality sodium bicarbonate injection treatments.
 Sale 27%
Sale 27%
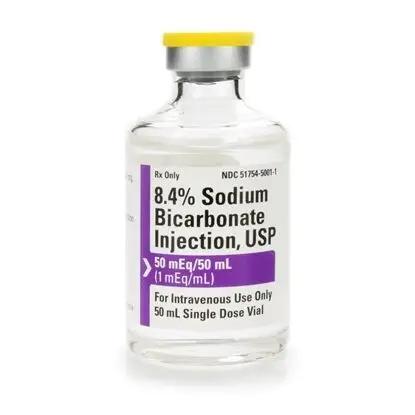
Sodium bicarbonate is a medication used to treat conditions caused by excessive acidity in the blood or urine, such as certain types of acidosis (a...
View full details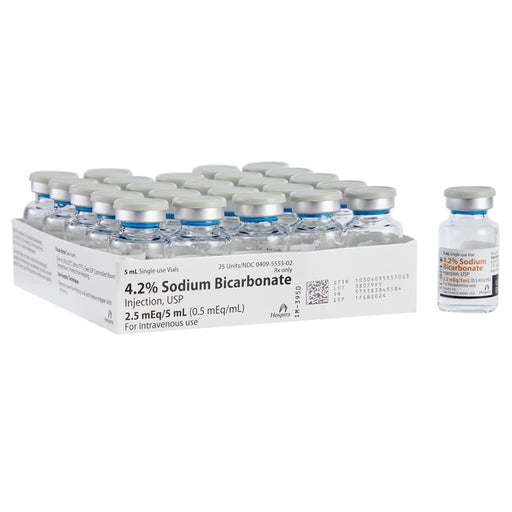 Sale 32%
Sale 32%
Sodium Bicarbonate 4.2% Injection is used to treat metabolic acidosis, a condition where the body produces excessive acid or the kidneys cannot rem...
View full details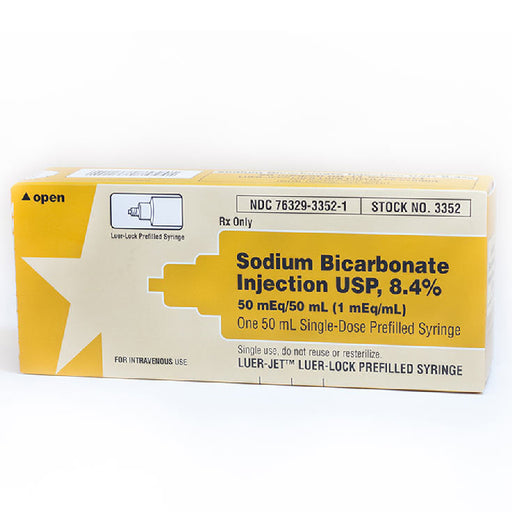 Sale 30%
Sale 30%
International Medication Systems 3352 Sodium Bicarbonate 8.4% Luer-Jet Prefilled Syringes 50 mL is a highly effective and widely used medication fo...
View full details Sale 30%
Sale 30%
Sodium Bicarbonate Injection 8.4% 10mL by Exela is a sterile, nonpyrogenic, and highly effective solution designed for the urgent management of lif...
View full details Sale 18%
Sale 18%
Exela Pharma Sodium Bicarbonate 4.2% Injection Single-Dose Vials 10 mL is an important medication in the field of medicine that plays a crucial rol...
View full details Sale 24%
Sale 24%
Hospira Sodium Bicarbonate for Injection 8.4% is a sterile, non-pyrogenic solution formulated for intravenous use in clinical and hospital settings...
View full details Sale 20%
Sale 20%
Hospira Sodium Bicarbonate Injection 4.2% is used to treat metabolic acidosis, a condition characterized by an excessive acid buildup in the body, ...
View full detailsDiscover premium Sodium Bicarbonate Injections—your trusted solution for acidosis treatment, pH balance, and metabolic correction. Our pharmaceutical-grade sodium bicarbonate offers rapid relief from severe metabolic acidosis, renal insufficiency, and cardiac arrest. Ideal for hospital, emergency, and clinical settings, these sterile injections help restore electrolyte balance, improve blood gas levels, and support critical care interventions. Ensure safe, effective patient management with our top-quality sodium bicarbonate injection treatments.
Buy Sodium Bicarbonate Injection Today – Secure Your Supply for Emergency & Critical Care Needs
Contact Us for Bulk Medical Orders, Hospital Inquiries, and Professional Support.
Treating severe metabolic acidosis. Managing certain drug overdoses. Correcting hyperkalemia related to renal failure. Used during cardiac arrest and CPR as part of emergency protocols. Sometimes used before epidural anesthesia to alkalinize solutions and reduce patient discomfort.
Typically, an infusion lasts from 30 minutes to several hours depending on clinical urgency and patient response. Emergency bolus doses act within minutes.
To quickly correct dangerous blood acidity, manage potassium toxicity, or counteract certain toxic ingestions and overdoses.
Limited data; should be used if clearly needed and the benefits outweigh risks. Consult with your obstetrician or healthcare provider.
Potential side effects include tissue irritation, hypokalemia, hypernatremia, metabolic alkalosis, volume overload, and possible complications in patients with heart or kidney disease. Rarely, improper administration can increase the risk of blood clots.
Prices vary by region, provider, and volume (typically $3–$40 per vial in the USA). Hospital charges may differ.
Prolonged/repeated use may lead to metabolic alkalosis, muscle twitching, electrolyte imbalance, or fluid overload. Routine use outside of acute hospital or dialysis settings is not recommended without close supervision.
The effect duration depends on the patient's metabolism and underlying conditions. A single dose acts within minutes and may last several hours.
Administer IV bolus or slow infusion under medical supervision. Only for use by qualified professionals, according to exact dosing protocols based on blood gas analysis.
To treat life-threatening acid-base disturbances, support resuscitation, or manage renal and critical care emergencies
Yes, occasionally mixed with local anesthetic solutions to speed onset and reduce injection pain during epidural anesthesia.
Rare, but improper administration or high doses may alter blood chemistry and potentially increase clotting risks.
Depending on cause: IV fluids, dialysis, other alkalinizing agents (e.g., tromethamine), and supportive care measures.
To rapidly reverse dangerously low blood pH, treat drug or toxin-induced acidosis, and stabilize patients in medical crisis.
Highest Purity & Safety Standards Used by Leading Hospitals & Emergency Rooms Trusted by Physicians Worldwide
Something went wrong. Please try again.
Check your email for exclusive offers and updates from Mountainside Medical.
